
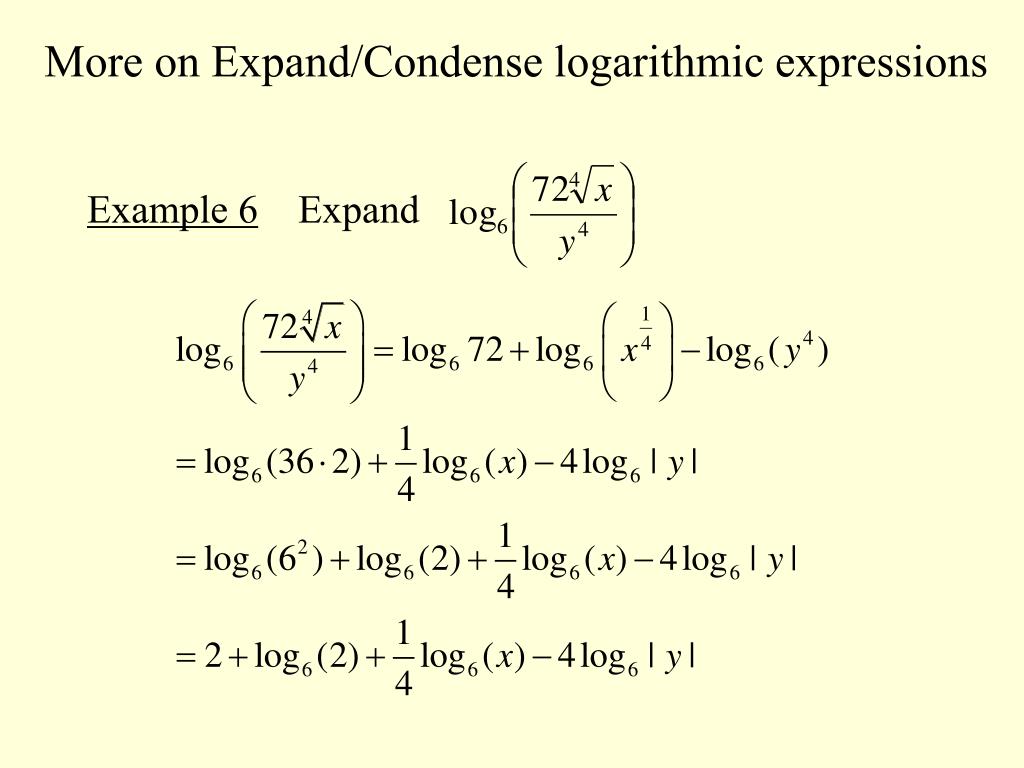
ln (6) − ln(2) ln ( 6) - ln ( 2) Use the quotient property of logarithms, logb (x)−logb(y) = logb( x y) log b ( x) - log b ( y) = log b ( x y). Simplify/Condense natural log of 6- natural log of 2. Simplify ( natural log of x)^2 ln2 (x) ln 2 ( x) Remove parentheses. The natural logarithm of x is the power to which e would have to be raised to equal x. The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln (x) or log e x.
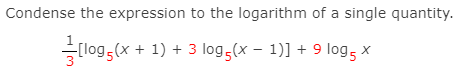
The number 'e' is an irrational constant approximately equal to 2.718281828459. Natural logarithm is particular case of logarithms and is typically used in solving time, growth/decay problems. 4 4.Detailed step by step solution for cosh(ln(2)) Please add a message. eln(22) e ln ( 2 2) Exponentiation and log are inverse functions. Evaluate e^ (2 natural log of 2) e2ln(2) e 2 ln ( 2) Simplify 2ln(2) 2 ln ( 2) by moving 2 2 inside the logarithm.
Log condense calculator with steps how to#
How to take the integral of ln^2(x) and how to check your solution.
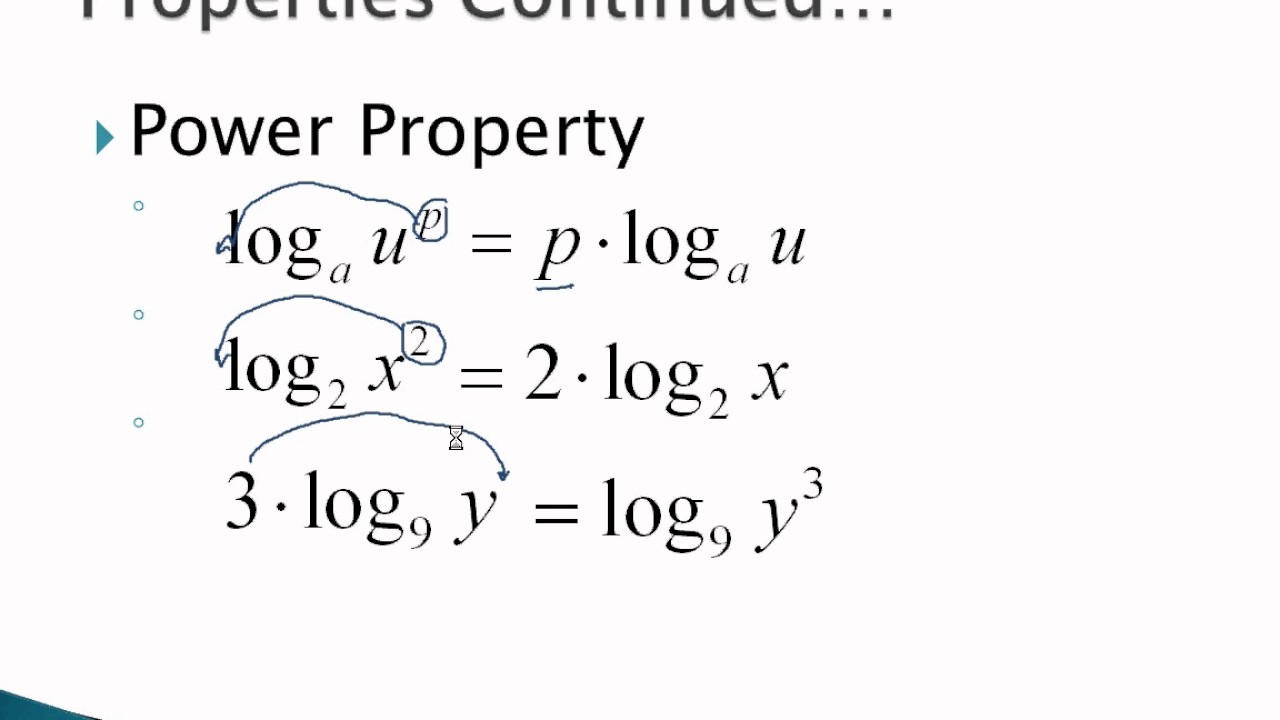
ln(3) ln ( 3) The result can be shown in multiple forms. $$ \ln \frac\right)^n = e $$How to take the integral of ln^2(x) and how to check your solution.Algebra.
Log condense calculator with steps download#
(Hint: take natural logarithm on both sides) To learn more values on common and natural logarithm, download BYJU’S – The Learning App and also learn maths shortcut tricks to learn with ease. If p = e 280 and q = e 300, prove that ln (ep 2 q –1) = 261.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
